Hornung Lab - Research
- Research
- Nucleic acid sensors
- Inflammasomes
- Genome Engineering
The Inflammasomes
Inflammasomes constitute a family of cytosolic sensors that can directly detect microbial molecules but also indirectly sense damage by detecting the perturbation of cellular homeostasis. Within recent years a lot of progress has been made in the characterization of inflammasome components and their pivotal role as surveillance machineries in the context of infection. Besides, it has become evident that many non-communicable diseases are triggered or perpetuated by inflammasomes and several studies have uncovered the great therapeutic potential of targeting these pathways. In that respect, inflammasomes have also become a prime focus for the development of novel anti-inflammatory therapies.
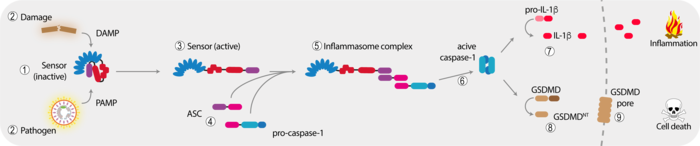
The minimal inflammasome signaling unit consists of a sensor protein and pro-caspase-1 that gets recruited to this sensor upon activation. Most inflammasomes, however, make use of the additional adapter protein ASC that serves to introduce a threshold-like signaling behavior and to amplify the response. The sensor protein itself often encodes for an oligomerization function that is engaged upon activation. This oligomerization of the sensor serves to form a seed-like structure that is required to initiate the assembly of a filamentous signal hub by the adapter protein ASC, which in turn recruits pro-caspase-1. In the case of NLR (nucleotide-binding domain and leucine-rich repeat-containing) proteins, it is the central NACHT domain that serves this function. Upon recruitment to the inflammasome complex, pro-caspase-1 is activated so that it can mature its substrates, such as the highly pro-inflammatory cytokine pro-IL-1β. Furthermore, caspase-1 cleaves the pore-forming molecule GSDMD, which triggers the lytic cell death of pyroptosis.
Next to its prominent role in processing of proinflammatory cytokine targets, caspase-1 also cleaves many other cytosolic proteins, the role of those is only starting to be understood. In our current projects we are mainly focusing on two inflammasome complexes: on the one hand, AIM2, a very specific sensor for cytosolic DNA and on the other hand NLRP3, a very important, yet up to now mechanistically poorly understood NLR sensor that responds to a large variety of cytoplasmic damage signals.
Using various complementary approaches, we are currently trying to understand their molecular mechanisms of activation and we aim at deciphering their functional roles at the cellular and organismic level in health and disease.
Recent publications in this area:
Vaccinia virus F1L blocks the ribotoxic stress response to subvert ZAKα-dependent NLRP1 inflammasome activation.
Szymanska I, Bauernfried S, Komar T, and Hornung V.
Eur J Immunol. 2024. doi: 10.1002/eji.202451135.
Pubmed
Hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis-like hyperinflammation due to a de novo mutation in DPP9.
Wolf C, Fischer H, Kühl JS, Koss S, Jamra RA, Starke S, Schultz J, Ehl S, Neumann K, Schuetz C, Huber R, Hornung V, and Lee-Kirsch MA.
J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2023. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2023.07.013.
Pubmed
IKKβ primes inflammasome formation by recruiting NLRP3 to the trans-Golgi network.
Schmacke NA, O'Duill F, Gaidt MM, Szymanska I, Kamper JM, Schmid-Burgk JL, Mädler SC, Mackens-Kiani T, Kozaki T, Chauhan D, Nagl D, Stafford CA, Harz H, Fröhlich AL, Pinci F, Ginhoux F, Beckmann R, Mann M, Leonhardt H, and Hornung V.
Immunity. 2022. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2022.10.021.
Pubmed
ZAKα-driven ribotoxic stress response activates the human NLRP1 inflammasome.
Robinson KS, Toh GA, Rozario P, Chua R, Bauernfried S, Sun Z, Firdaus MJ, Bayat S, Nadkarni R, Poh ZS, Tham KC, Harapas CR, Lim CK, Chu W, Tay CWS, Tan KY, Zhao T, Bonnard C, Sobota R, Connolly JE, Common J, Masters SL, Chen KW, Ho L, Wu B, Hornung V, and Zhong FL.
Science. 2022. doi: 10.1126/science.abl6324.
Pubmed
Post-injury immunosuppression and secondary infections are caused by an AIM2 inflammasome-driven signaling cascade.
Roth S, Cao J, Singh V, Tiedt S, Hundeshagen G, Li T, Boehme JD, Chauhan D, Zhu J, Ricci A, Gorka O, Asare Y, Yang J, Lopez MS, Rehberg M, Bruder D, Zhang S, Groß O, Dichgans M, Hornung V, and Liesz A.
Immunity. 2021. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2021.02.004.
Pubmed
Human NLRP1 is a sensor for double-stranded RNA.
Bauernfried S, Scherr MJ, Pichlmair A, Duderstadt KE, and Hornung V.
Science. 2021. pii: eabd0811. doi: 10.1126/science.abd0811.
Pubmed
Inflammasome-Dependent Induction of Adaptive NK Cell Memory.
van den Boorn JG, Jakobs C, Hagen C, Renn M, Luiten RM, Melief CJ, Tüting T, Garbi N, Hartmann G, and Hornung V.
Immunity. 2016. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2016.05.008.
Pubmed
Human Monocytes Engage an Alternative Inflammasome Pathway.
Gaidt MM, Ebert TS, Chauhan D, Schmidt T, Schmid-Burgk JL, Rapino F, Robertson AA, Cooper MA, Graf T, and Hornung V.
Immunity. 2016. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2016.01.012.
Pubmed
A Genome-wide CRISPR (Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats) Screen Identifies NEK7 as an Essential Component of NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation.
Schmid-Burgk JL, Chauhan D, Schmidt T, Ebert TS, Reinhardt J, Endl E, and Hornung V.
J Biol Chem. 2016. doi: 10.1074/jbc.C115.700492.
Pubmed
Selected reviews in this area:
A critical role for palmitoylation in pyroptosis.
Sun Z, and Hornung V.
Mol Cell. 2024. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2024.05.023.
Pubmed
The NLRP3 Inflammasome Renders Cell Death Pro-inflammatory.
Gaidt MM, and Hornung V.
J Mol Biol. 2018. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2017.11.013.
Pubmed
Alternative inflammasome activation enables IL-1β release from living cells.
Gaidt MM, and Hornung V.
Curr Opin Immunol. 2017. doi: 10.1016/j.coi.2016.10.007.
Pubmed
Pore formation by GSDMD is the effector mechanism of pyroptosis.
Gaidt MM, and Hornung V.
EMBO J. 2016. N/A.
Pubmed